常见集合总结
常见集合总结
提示
放本地文件夹都快吃土了,准备清理文件夹,发现还有笔记上传下吧!关于集合的
该部分参考 菜鸟教程 (opens new window)
集合框架被设计成要满足以下几个目标。
- 该框架必须是高性能的。基本集合(动态数组,链表,树,哈希表)的实现也必须是高效的。
- 该框架允许不同类型的集合,以类似的方式工作,具有高度的互操作性。
- 对一个集合的扩展和适应必须是简单的。
# 集合接口
集合框架定义了一些接口。本节提供了每个接口的概述:
| 序号 | 接口描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Collection 接口 Collection 是最基本的集合接口,一个 Collection 代表一组 Object,即 Collection 的元素, Java不提供直接继承自Collection的类,只提供继承于的子接口(如List和set)。Collection 接口存储一组不唯一,无序的对象。 |
| 2 | List 接口 List接口是一个有序的 Collection,使用此接口能够精确的控制每个元素插入的位置,能够通过索引(元素在List中位置,类似于数组的下标)来访问List中的元素,第一个元素的索引为 0,而且允许有相同的元素。List 接口存储一组不唯一,有序(插入顺序)的对象。 |
| 3 | Set Set 具有与 Collection 完全一样的接口,只是行为上不同,Set 不保存重复的元素。Set 接口存储一组唯一,无序的对象。 |
| 4 | SortedSet 继承于Set保存有序的集合。 |
| 5 | Map Map 接口存储一组键值对象,提供key(键)到value(值)的映射。 |
| 6 | Map.Entry 描述在一个Map中的一个元素(键/值对)。是一个 Map 的内部接口。 |
| 7 | SortedMap 继承于 Map,使 Key 保持在升序排列。 |
| 8 | Enumeration 这是一个传统的接口和定义的方法,通过它可以枚举(一次获得一个)对象集合中的元素。这个传统接口已被迭代器取代。 |
标准集合类汇总于下表:
| 序号 | 类描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | AbstractCollection 实现了大部分的集合接口。 |
| 2 | AbstractList 继承于AbstractCollection 并且实现了大部分List接口。 |
| 3 | AbstractSequentialList 继承于 AbstractList ,提供了对数据元素的链式访问而不是随机访问。 |
| 4 | LinkedList (opens new window) 该类实现了List接口,允许有null(空)元素。主要用于创建链表数据结构,该类没有同步方法,如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步,解决方法就是在创建List时候构造一个同步的List。例如: |
| 5 | ArrayList (opens new window) 该类也是实现了List的接口,实现了可变大小的数组,随机访问和遍历元素时,提供更好的性能。该类也是非同步的,在多线程的情况下不要使用。ArrayList 增长当前长度的50%,插入删除效率低。 |
|---|---|
| 6 | AbstractSet 继承于AbstractCollection 并且实现了大部分Set接口。 |
| 7 | HashSet (opens new window) 该类实现了Set接口,不允许出现重复元素,不保证集合中元素的顺序,允许包含值为null的元素,但最多只能一个。 |
| 8 | LinkedHashSet 具有可预知迭代顺序的Set接口的哈希表和链接列表实现。 |
| 9 | TreeSet 该类实现了Set接口,可以实现排序等功能。 |
| 10 | AbstractMap 实现了大部分的Map接口。 |
| 11 | HashMap (opens new window) HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。 该类实现了Map接口,根据键的HashCode值存储数据,具有很快的访问速度,最多允许一条记录的键为null,不支持线程同步。 |
| 12 | TreeMap 继承了AbstractMap,并且使用一颗树。 |
| 13 | WeakHashMap 继承AbstractMap类,使用弱密钥的哈希表。 |
| 14 | LinkedHashMap 继承于HashMap,使用元素的自然顺序对元素进行排序. |
| 15 | IdentityHashMap 继承AbstractMap类,比较文档时使用引用相等。 |
集合图
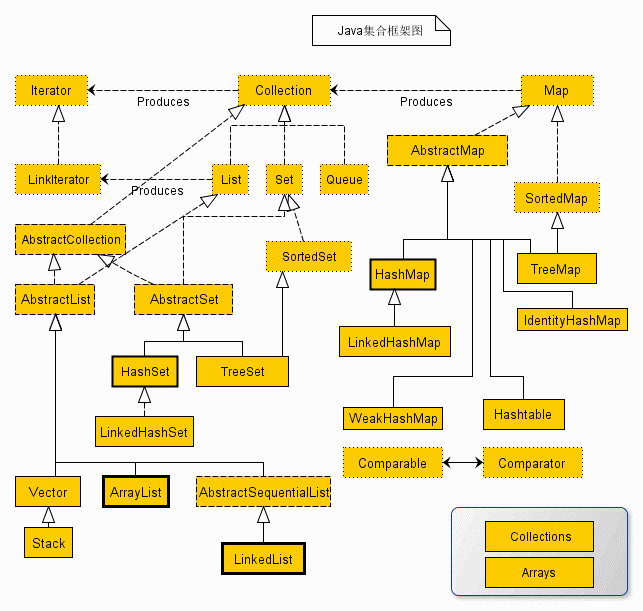
# List
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Vector
- Stack
# ArrayList
继承图
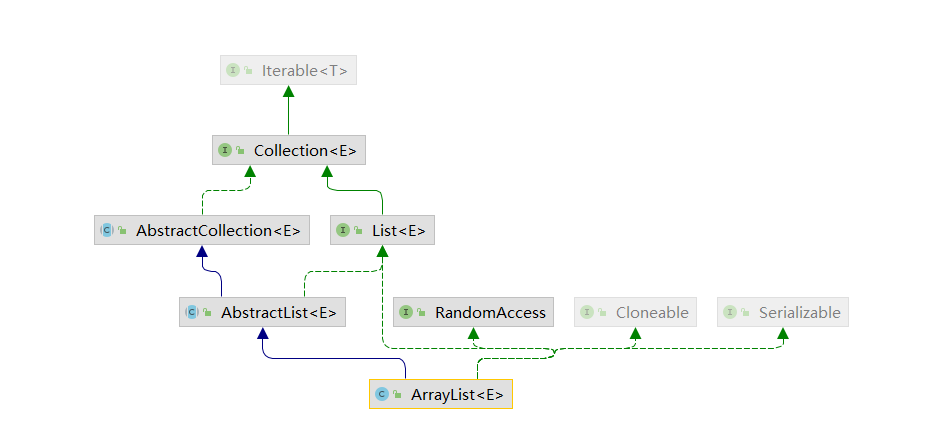
最基本的list,底层是数组 new Object[]
// 默认构造方法,可以默认指定容量
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/* private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};*/
2
3
4
5
迭代器
// ArrayList返回的迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
// Itr是ArrayList的一个内部类,实现了Iterator接口,内部实现参考源代码
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# LinkedList
继承图
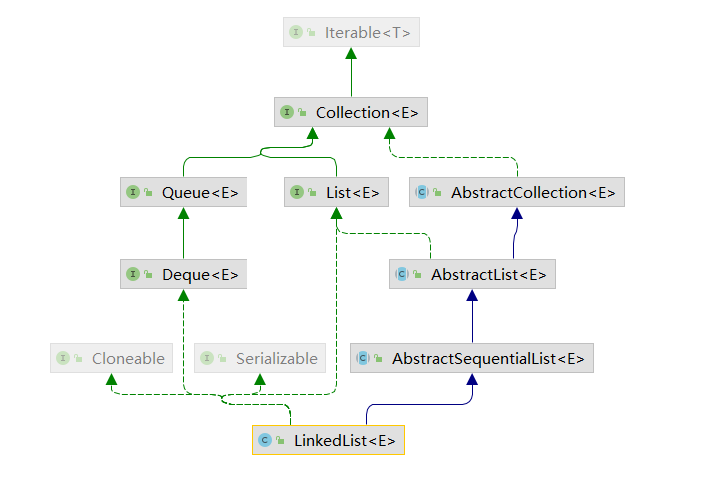
底层是节点 包含自身,上一个节点和下一关节点
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
迭代器
// linkedlist 的listIterator 方法
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
// ListItr 是 linkedlist 内部类
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {}
// ListIterator继承了Iterator
public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E> {
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Vector
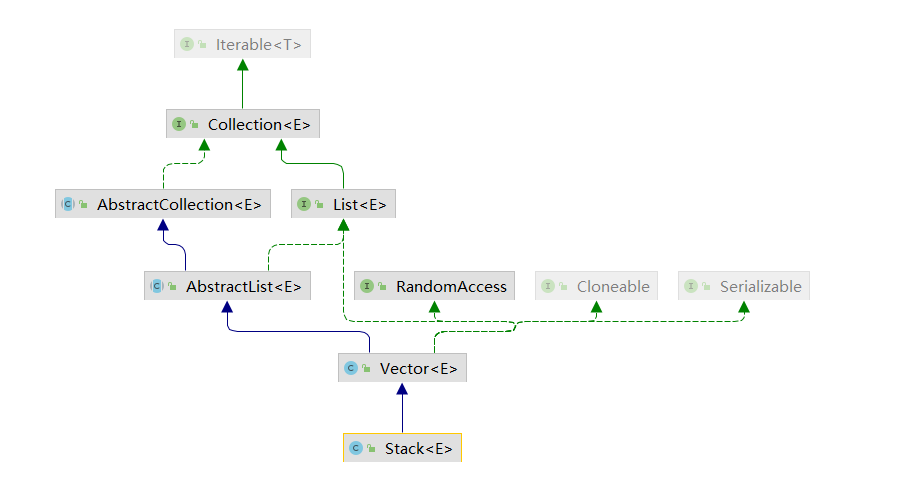
底存也是数组,不过相关方法添加了关键词 synchronized,所以操作时候效率较ArrayList效率低
/*其中一个构造方法*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
以为 add方法为例
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
迭代器
public synchronized Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
// 内部实现请参考源代码
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {}
2
3
4
5
6
# Stack

继承了Vector,因此具有Vector的特点
/*
Stack类表示对象的后进先出 (LIFO) 堆栈。它使用五个操作扩展类Vector ,这些操作允许将向量视为堆栈。提供了通常的push和pop操作,以及查看堆栈顶部项目的方法,测试堆栈是否为空的方法,以及在堆栈中搜索项目并发现它有多远的方法是从顶部。
首次创建堆栈时,它不包含任何项目。
*/
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E>{}
2
3
4
5
# Map
- HashMap
- HashTable
# HashMap
底层是哈希表,
HashMap的实例有两个影响其性能的参数:初始容量和负载因子
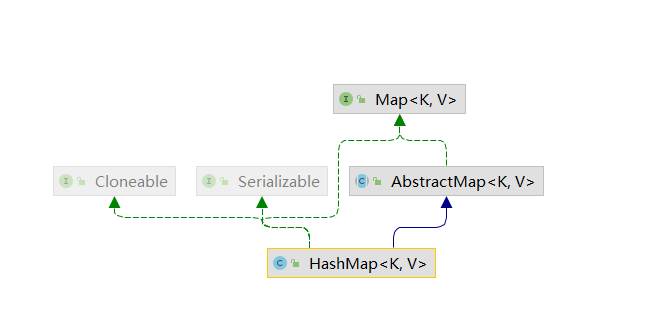
核心构造方法
// 存放内容
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 容量判断
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor; // 负载因子 默认 0.75f
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
// 内部类table 的基本内容
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
put方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
// 初始化
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 初始化判断,如果table内容为null或者长度为0 给个初始容量 默认为 16
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 根据长度和 hashcode与运算,计算索引,如果tabl[index]内容为null 生成一个节点
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
// 初始化
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 如果内容不为null计算 hashcode与key是否相等 或者 key.equal(k) ==> k=p.key
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 判断是否是树化节点,如果是树化节点,根据treeNode类添加
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 遍历
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 遍历判断 hashCode和 key是否相等 或者 key.equals(k) => k=e.key
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 判断是否生成了e 如果e!=null
if (e != null) {
// 保存 原来value
V oldValue = e.value;
// 存在节点同时,内容 是否为空或者 oblyIfAbsent 是否修改当前值 默认为false
// !onlyIfAbsent = true ,默认修改值
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 判断容量是否超过 如果超过了容量扩大两倍
// threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
树节点类
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
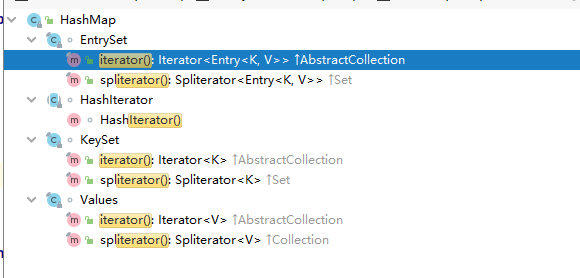
HashMap 主要 有三种 迭代器,这里迭代器有 key 的迭代器,和 value的迭代器
# HashTable
继承图
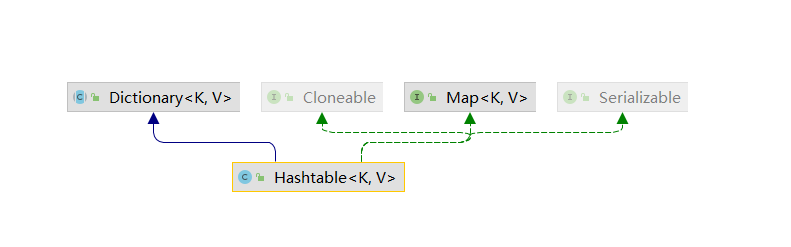
HashTable核心构造函数
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 容量初始化判断 不能小于0 而且必须是 float类型数据
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
hashtable 的 put方法和内部类
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 通过计算得到 索引
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
// 遍历比较 值 如果不为null 更新 原来只
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
// 如果遍历没有返回 添加 到 hashtable中
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
// Hashtable 静态内部类 Entry
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
其他方法参考Hashtable源代码
# TreeMap
TreeMap 基于 NavigableMap实现了红黑树,实现了SortMap因此,具有顺序
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Set
- HashSet
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet
# HashSet
继承图
底层是HashMap,因此value相当于是 map的key,map的value 值是固定为 PRESENT, 因此,不允许重复!是无序的。
// HashSet其中一个构造方法
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
// add 调用的是hashmap put方法,其中 PRESENT = new Object();
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
//迭代器 迭代器使用的是map的迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
// keySet 是 HashMap 一个内部类 具体内容参考HashMap源代码
final class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# LinkedHashSet
继承了 HashSet,此实现与HashSet的不同之处在于它维护一个双向链表,该列表贯穿其所有条目。这个链表定义了迭代顺序,即元素插入集合的顺序(插入顺序)。请注意,如果将元素重新插入集合中,则插入顺序不受影响。 (如果s.add(e)被调用,而s.contains(e)将在调用之前立即返回true ,则元素e被重新插入到集合s中。)
public class LinkedHashSet<E>
extends HashSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
2
3
# TreeSet
继承图
底层是 treemap
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
// add
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
// 迭代器
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
set和List区别
Set 接口实例存储的是无序的,不重复的数据。List 接口实例存储的是有序的,可以重复的元素。
Set 检索效率低下,删除和插入效率高,插入和删除不会引起元素位置改变
List 和数组类似,可以动态增长,根据实际存储的数据的长度自动增长 List 的长度。查找元素效率高,插入删除效率低,因为会引起其他元素位置改变
SortedSet
元素使用它们的自然顺序排序,或者由通常在排序集创建时提供的Comparator排序。集合的迭代器将按元素升序遍历集合。
- KeySet
// TreeMap 的一个静态内部类
static final class KeySet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements NavigableSet<E> {}
2