 位运算相关总结
位运算相关总结
#
# 集合基本概念
| 术语 | 集合 | 位运算 | 举例1 | 举例2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 交集 | A∩B | a&b | {0,2,3} ∩ {0,1,2} = {0,2} | 1101 & 0111 = 0101 |
| 并集 | A∪B | a ∣ b | {0,2,3} ∪ {0,1,2} = {0,1,2,3} | 1101 | 0111 = 1111 |
| 对称差 | A Δ B | a⊕b | {0,2,3} Δ {0,1,2} = {1,3} | 1101 ⊕ 0111 = 1111 |
| 差 | A∖B | a&∼b | {0,2,3} \ {1,2} = {0,3} | 1101 & 0111 = 1001 |
| 差(子集) | A∖B (B ⊆ A) | a⊕b | {0,2,3} \ {0,2} = {3} | 1101 ⊕ 0101 = 1000 |
| 包含于 | A⊆B | a&b=a a ∣ b=b | {0,2} ⊆ {0,2,3} | 0101 & 1101 = 0101 , 0101 | 1101 = 1101 |
其中 & 表示按位与,∣ 表示按位或,⊕ 表示按位异或,∼ 表示按位取反。
# 集合与位运算
S 为集合 i 为元素
| 术语 | 集合 | 位运算 | 举例1 | 举例2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 空集 | ∅ | 0 | ||
| 单元素集合 | {i} | 1<<i | {2} | 1<<2 |
| 全集 | {0,1,2,...,n-1} | (1<<n)-1 | {0,1,2,3} | (1<<4)-1 |
| 补集 | ∁U**S=U∖S | ~s | ||
| 属于 | i∈S | (s>>i)&1 == 1 | 2∈ {0,1,2,3} | 1111>>2&1 = 1 |
| 不属于 | i∈/ s | (s>>i)&1 == 0 | 4∈/ {0,1,2,3} | 1111>>4&1 = 0 |
| 添加元素 | S∪{i} | s ∣ (1 << i) | {0,3}∪{2} | 1001 ∣ (1 << 2) |
| 删除元素 | S∖{i} | s&∼(1 << i) | {0,2,3}∖{2} | 1101&∼(1 << 2) |
| 删除元素 | S∖{i} (i∈S) | s⊕(1 << i) | {0,2,3}∖{2} | 1101⊕(1 << 2) |
| 获取最低位 | i & ~i | |||
| 删除最小元素 | s&(s−1) | 1110 & (1110 - 0001) = 1100 |
其中 & 表示按位与,∣ 表示按位或,⊕ 表示按位异或,∼ 表示按位取反。
# 其他操作
# 检查单独出现
a ^ a = 0
a ^ 0 = a
1
2
2
因此有相关定义
假设集合S中其他元素都出现了偶数次,只有元素a出现了一次,请找出a
public static void check() {
int[] arr = {1,1,2,2,3,4,3,6,6};
int ans = arr[0];
for(int i =1;i<arr.length;i++) {
ans ^= arr[i];
// 出现偶数次根据上面定义会被自己消除
// 最后只剩小 0 和 a
// 因此 能找到 a
}
System.out.println("ONE = " + ans);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 获取1出现的个数
// 普通实现方式
public static int bitCount(int i) {
int cnt = 0;
while (i != 0) {
i &= i - 1;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
// JDK Integer类 实现方式 当然看不懂了,不过效率肯定比while方式快!
public static int bitCount(int i) {
// HD, Figure 5-2
i = i - ((i >>> 1) & 0x55555555);
i = (i & 0x33333333) + ((i >>> 2) & 0x33333333);
i = (i + (i >>> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f;
i = i + (i >>> 8);
i = i + (i >>> 16);
return i & 0x3f;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 获取最低位
// 可以参见 JDK Integer类 源码
public static int lowestOneBit(int i) {
return i & -i;
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# 获取最高位
// 可以参见 JDK Integer类 源码
public static int highbit(int i) {
i |= (i >> 1);
i |= (i >> 2);
i |= (i >> 4);
i |= (i >> 8);
i |= (i >> 16);
i -= (i >>> 1)
return i ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 更多技巧
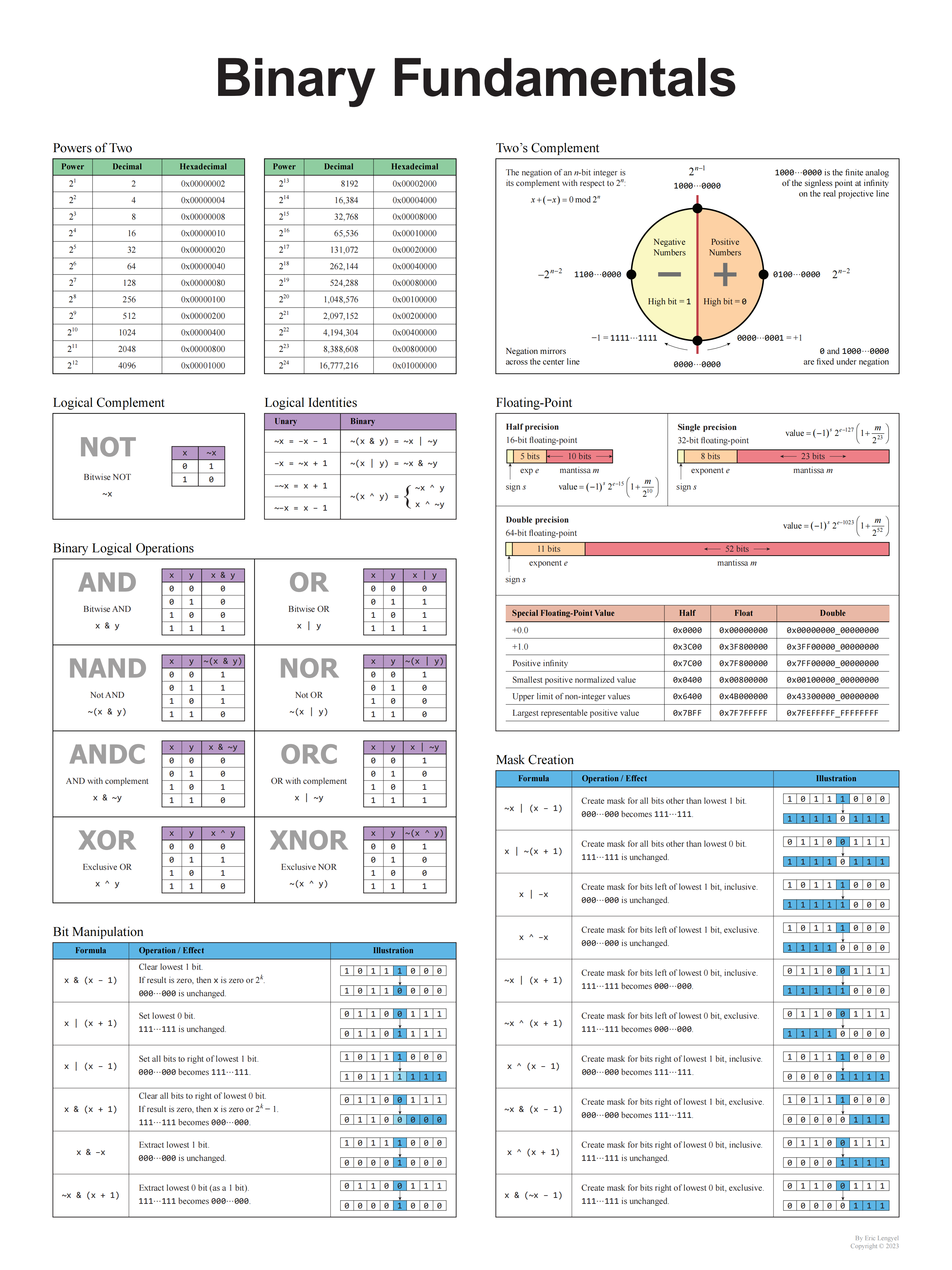
# 相关例题
# 第一个出现两次字母 easy
思路分析
- 字符串的字符本质是数字 可以使用 s>>i&1 == 1 判断是否出现 对于不存在i的添加 s |= 1<<i
public char repeatedCharacter(String s) {
int mask = 1 << (s.charAt(0) - '0');
for(int i = 1;i<s.length();i++){
int idx = s.charAt(i) - '0';
if( (mask >> idx & 1) == 0){
mask |= 1 << idx;
continue;
}
return s.charAt(i);
}
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 至少出现一次的数字 hard
思路分析
- 至少出现一次的数字 = 总数 - 枚举一次都没有出现的重复数字
- 动态规划当前位数
- 注意非数字的特殊情况
class Solution {
char[] nums;
int[][] dp;
public int numDupDigitsAtMostN(int n) {
this.nums = String.valueOf(n).toCharArray();
this.dp = new int[nums.length][1<<10];
for(int i = 0;i<nums.length;i++) Arrays.fill(dp[i],-1);
return n - dfs(0,0,true,false);
}
public int dfs(int idx,int mask,boolean isLimit,boolean isNumber){
if( idx == nums.length ) {
return isNumber ? 1 : 0;
}
if( !isLimit && isNumber && dp[idx][mask] != -1 ) return dp[idx][mask];
int ans = 0;
if( !isNumber){
ans = dfs(idx + 1,mask,false,false);
}
int up = isLimit ? nums[idx] - '0' : 9;
for(int di = isNumber ? 0 : 1;di<=up;di++){
if( ( (mask>>di) & 1) == 0){
ans += dfs(idx+1,mask | (1 << di),isLimit && up == di,true);
}
}
if( !isLimit && isNumber) dp[idx][mask] = ans;
return ans;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
参考链接
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2025-06-24, 01:16:46